The Problem
LLMs stream JSON token by token. Your structured output arrives as:
{"project": {"name": "Mo
{"project": {"name": "Mobile App", "status": "in_prog
{"project": {"name": "Mobile App", "status": "in_progress"}, "tasks": [{"title": "UI Redes
...
Standard encoding/json fails on every chunk except the last:
json.Unmarshal([]byte(`{"project": {"name": "Mo`), &result)
// error: unexpected end of JSON input
This was recently highlighted by swyx as a #1 or #2 performance issue in AI applications. You’re forced to wait for the complete response before showing anything to users - negating the entire point of streaming with json mode or structured output.
📄 View full demo code
package main
import (
"encoding/json"
"fmt"
"math/rand"
"time"
)
type Task struct {
Title string `json:"title"`
Status string `json:"status"`
Priority string `json:"priority"`
}
type Project struct {
Name string `json:"name"`
Status string `json:"status"`
}
type Response struct {
Project Project `json:"project"`
Tasks []Task `json:"tasks"`
Summary string `json:"summary"`
Score float64 `json:"score"`
}
func randomSleep() {
ms := 10 + rand.Intn(91) // 10-100ms
time.Sleep(time.Duration(ms) * time.Millisecond)
}
func main() {
rand.Seed(time.Now().UnixNano())
chunks := []string{
`{"project":`,
` {"name": "Mo`,
`bile App", "`,
`status": "in`,
`_progress"},`,
` "tasks": [{`,
`"title": "UI`,
` Redesign",`,
` "status": "`,
`done", "prio`,
`rity": "high`,
`"}, {"title"`,
`: "API Inte`,
`gration", "s`,
`tatus": "in_`,
`progress", "`,
`priority": "`,
`medium"}], "`,
`summary": "P`,
`roject is on`,
` track with `,
`good progres`,
`s.", "score"`,
`: 0.85}`,
}
fmt.Println("╔════════════════════════════════════════════════════════════╗")
fmt.Println("║ encoding/json - Parsing Streaming LLM Output ║")
fmt.Println("╚════════════════════════════════════════════════════════════╝")
fmt.Println()
fmt.Println("Waiting for valid JSON...")
fmt.Println()
var buffer string
var result Response
startTime := time.Now()
var timeToFirstOutput time.Duration
for i, chunk := range chunks {
buffer += chunk
randomSleep()
err := json.Unmarshal([]byte(buffer), &result)
if err == nil {
timeToFirstOutput = time.Since(startTime)
fmt.Print("\033[2J\033[H") // Clear screen
fmt.Println("╔════════════════════════════════════════════════════════════╗")
fmt.Println("║ encoding/json - Parsing Streaming LLM Output ║")
fmt.Println("╚════════════════════════════════════════════════════════════╝")
fmt.Println()
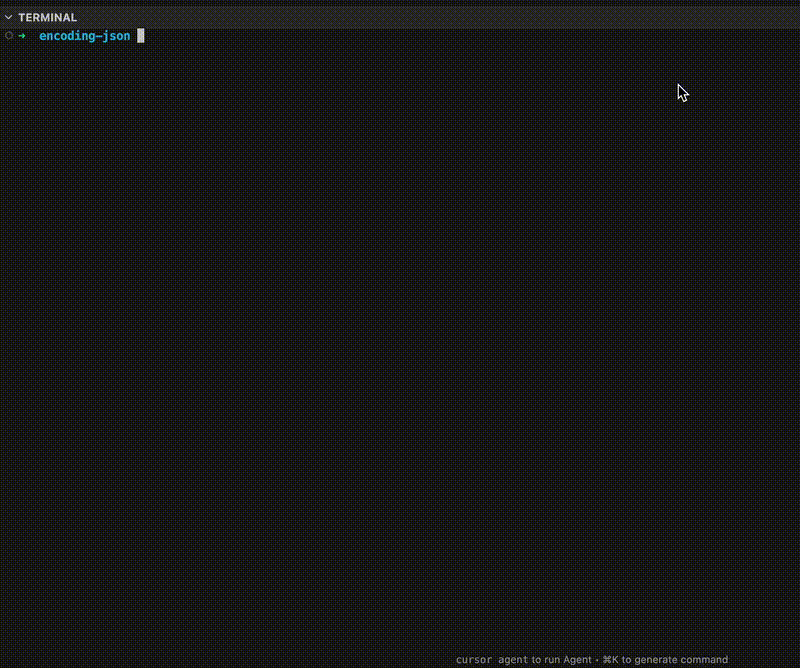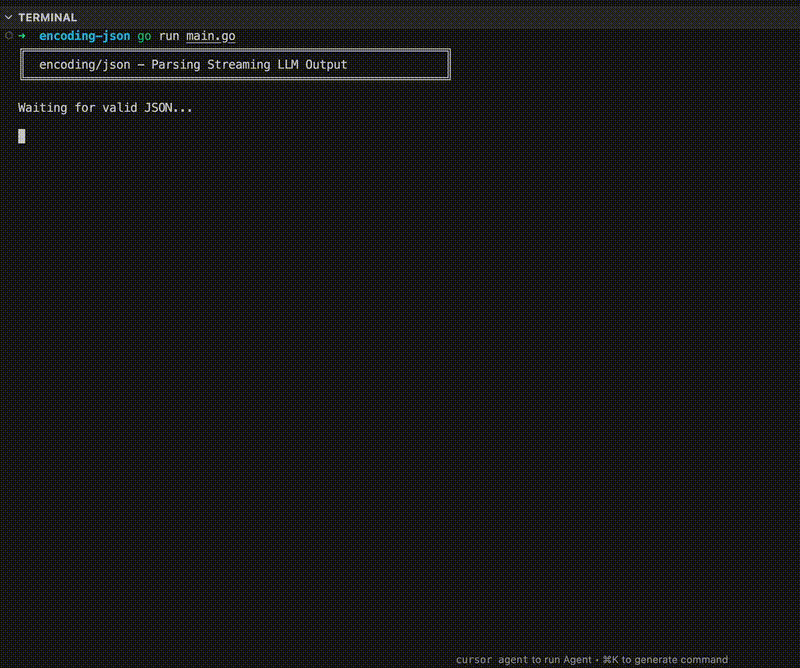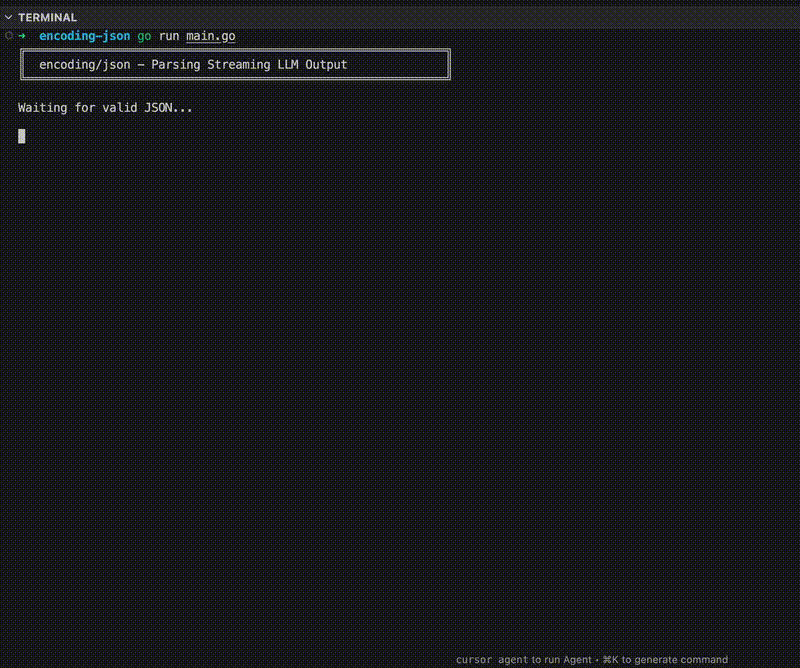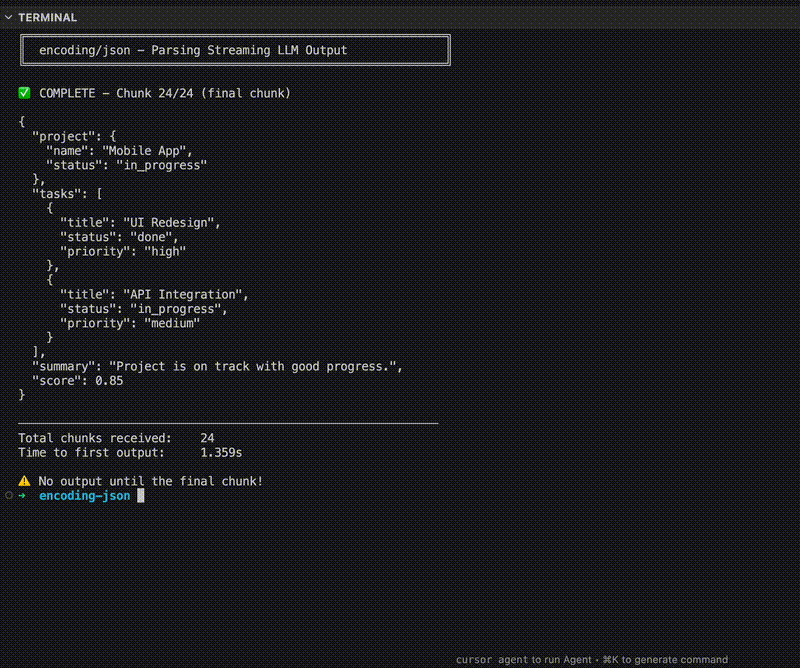
fmt.Printf("✅ COMPLETE - Chunk %d/%d (final chunk)\n", i+1, len(chunks))
fmt.Println()
prettyJSON, _ := json.MarshalIndent(result, "", " ")
fmt.Println(string(prettyJSON))
}
}
fmt.Println()
fmt.Println("────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────")
fmt.Printf("Total chunks received: %d\n", len(chunks))
fmt.Printf("Time to first output: %v\n", timeToFirstOutput.Round(time.Millisecond))
fmt.Println()
fmt.Println("⚠️ No output until the final chunk!")
}
The Solution
godantic provides StreamParser - a streaming JSON parser that repairs incomplete JSON, tracks which fields are still coming, and validates on the fly.
parser := godantic.NewStreamParser[Response]()
for chunk := range llmStream {
result, state, _ := parser.Feed(chunk)
if state.IsComplete {
fmt.Println("Done:", result)
} else {
// Shows: ["project.status", "tasks[1].title", ...]
fmt.Printf("Waiting for: %v\n", state.WaitingFor())
}
}
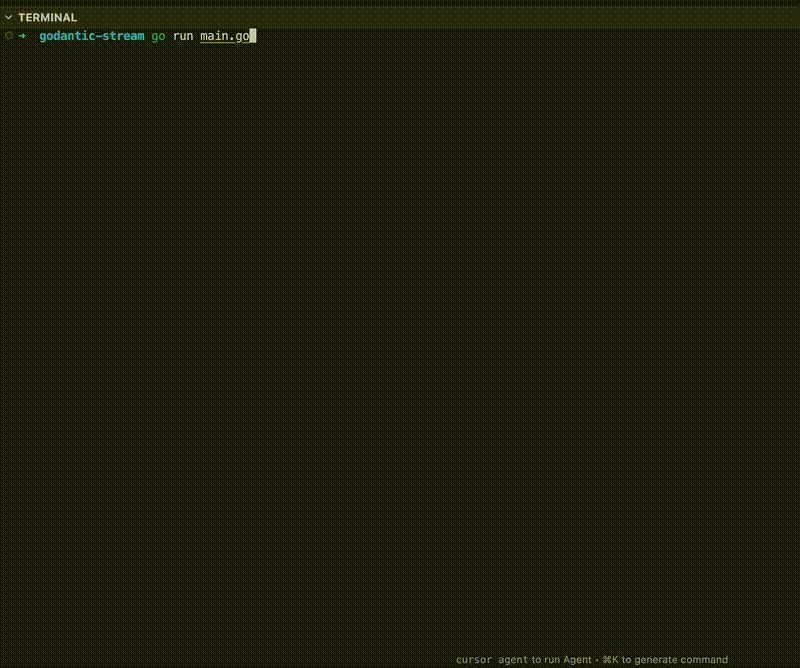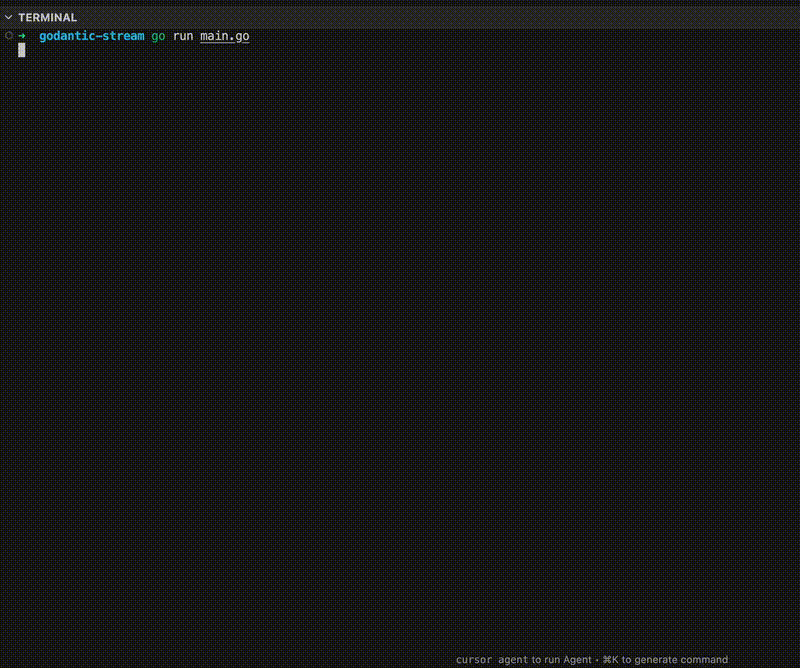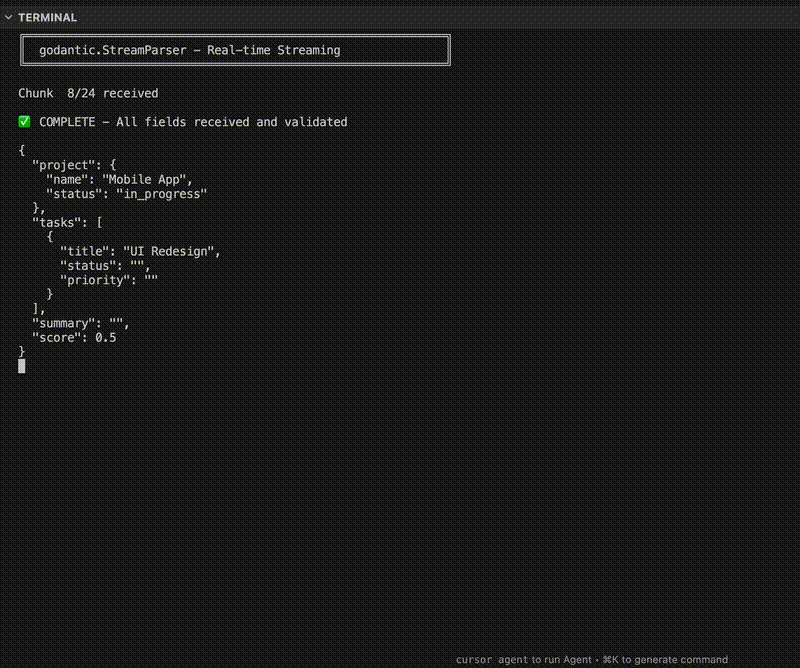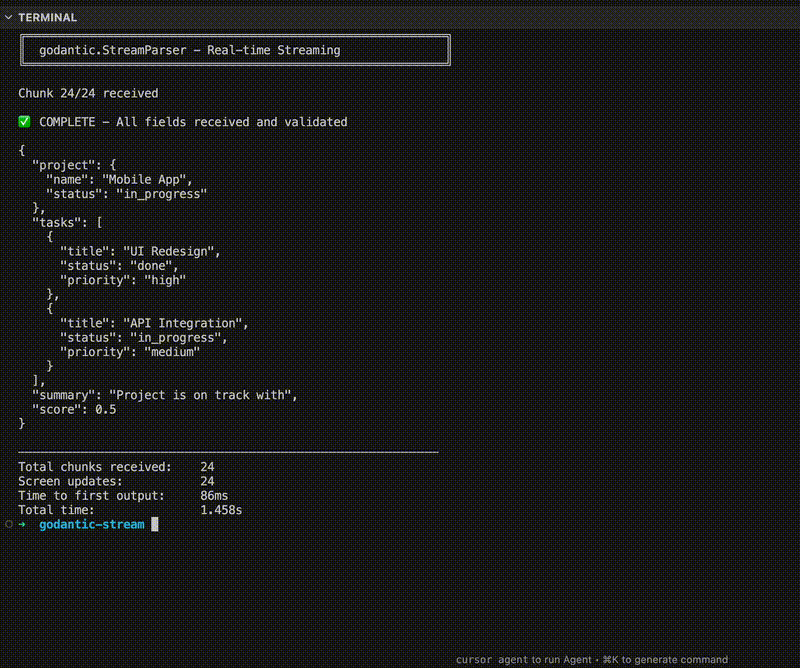
With godantic: nested fields populate in real-time as tokens arrive.
Time to first output drops from seconds to milliseconds - you’re no longer waiting for the complete response. This is a simple example, but the gains are significant for long generations where users would otherwise stare at a blank screen.
📄 View full demo code
package main
import (
"encoding/json"
"fmt"
"math/rand"
"time"
"github.com/deepankarm/godantic/pkg/godantic"
)
type Task struct {
Title string `json:"title"`
Status string `json:"status"`
Priority string `json:"priority"`
}
type Project struct {
Name string `json:"name"`
Status string `json:"status"`
}
type Response struct {
Project Project `json:"project"`
Tasks []Task `json:"tasks"`
Summary string `json:"summary"`
Score float64 `json:"score"`
}
func (r *Response) FieldScore() godantic.FieldOptions[float64] {
return godantic.Field(
godantic.Default(0.5),
godantic.Min(0.0),
godantic.Max(1.0),
)
}
func randomSleep() {
ms := 10 + rand.Intn(91) // 10-100ms
time.Sleep(time.Duration(ms) * time.Millisecond)
}
func main() {
rand.Seed(time.Now().UnixNano())
chunks := []string{
`{"project":`,
` {"name": "Mo`,
`bile App", "`,
`status": "in`,
`_progress"},`,
` "tasks": [{`,
`"title": "UI`,
` Redesign",`,
` "status": "`,
`done", "prio`,
`rity": "high`,
`"}, {"title"`,
`: "API Inte`,
`gration", "s`,
`tatus": "in_`,
`progress", "`,
`priority": "`,
`medium"}], "`,
`summary": "P`,
`roject is on`,
` track with `,
`good progres`,
`s.", "score"`,
`: 0.85}`,
}
parser := godantic.NewStreamParser[Response]()
startTime := time.Now()
var timeToFirstOutput time.Duration
updateCount := 0
for i, chunk := range chunks {
randomSleep()
result, state, _ := parser.Feed([]byte(chunk))
if result == nil {
continue
}
updateCount++
if timeToFirstOutput == 0 {
timeToFirstOutput = time.Since(startTime)
}
fmt.Print("\033[2J\033[H") // Clear screen
fmt.Println("╔════════════════════════════════════════════════════════════╗")
fmt.Println("║ godantic.StreamParser - Real-time Streaming ║")
fmt.Println("╚════════════════════════════════════════════════════════════╝")
fmt.Println()
fmt.Printf("Chunk %2d/%d received\n", i+1, len(chunks))
fmt.Println()
if state.IsComplete {
fmt.Println("✅ COMPLETE - All fields received and validated")
} else {
waiting := state.WaitingFor()
if len(waiting) > 0 {
fmt.Printf("⏳ STREAMING - Waiting for: %s\n", waiting[0])
if len(waiting) > 1 {
fmt.Printf(" (and %d more fields)\n", len(waiting)-1)
}
}
}
fmt.Println()
currentJSON, _ := json.MarshalIndent(result, "", " ")
fmt.Println(string(currentJSON))
}
totalTime := time.Since(startTime)
fmt.Println()
fmt.Println("────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────")
fmt.Printf("Total chunks received: %d\n", len(chunks))
fmt.Printf("Screen updates: %d\n", updateCount)
fmt.Printf("Time to first output: %v\n", timeToFirstOutput.Round(time.Millisecond))
fmt.Printf("Total time: %v\n", totalTime.Round(time.Millisecond))
}
How It Works
- Repairs incomplete JSON - closes unclosed strings, arrays, objects at any nesting level
- Tracks incomplete fields -
state.WaitingFor()returns paths like["project.name", "tasks[1].status"] - Skips validation for incomplete fields - no false errors mid-stream
- Applies defaults automatically - sensible fallbacks while data streams
The parser accumulates chunks internally, so each Feed() call returns the current best-effort parse of everything received so far.
Typed Schemas for LLMs
godantic also generates JSON schemas from your Go types - useful for LLM structured output:
type Response struct {
Project Project `json:"project"`
Tasks []Task `json:"tasks"`
Summary string `json:"summary"`
Score float64 `json:"score"`
}
func (r *Response) FieldScore() godantic.FieldOptions[float64] {
return godantic.Field(
godantic.Default(0.5),
godantic.Min(0.0),
godantic.Max(1.0),
)
}
// Generate schema for Gemini/OpenAI/Anthropic
schemaGen := schema.NewGenerator[Response]()
jsonSchema, err := schemaGen.GenerateFlattened()
The same types work for schema generation and streaming parse - one definition, used everywhere.
Try It
go get github.com/deepankarm/godantic
See the streaming example for a complete working demo with Gemini.